How Inflation Affects the Housing Market
Have you ever thought about how inflation affects the housing market? They are, believe it or not, linked. When one is changed, the other is affected. Here's a high-level outline of the two's relationship.
The Connection Between Housing and Overall Inflation
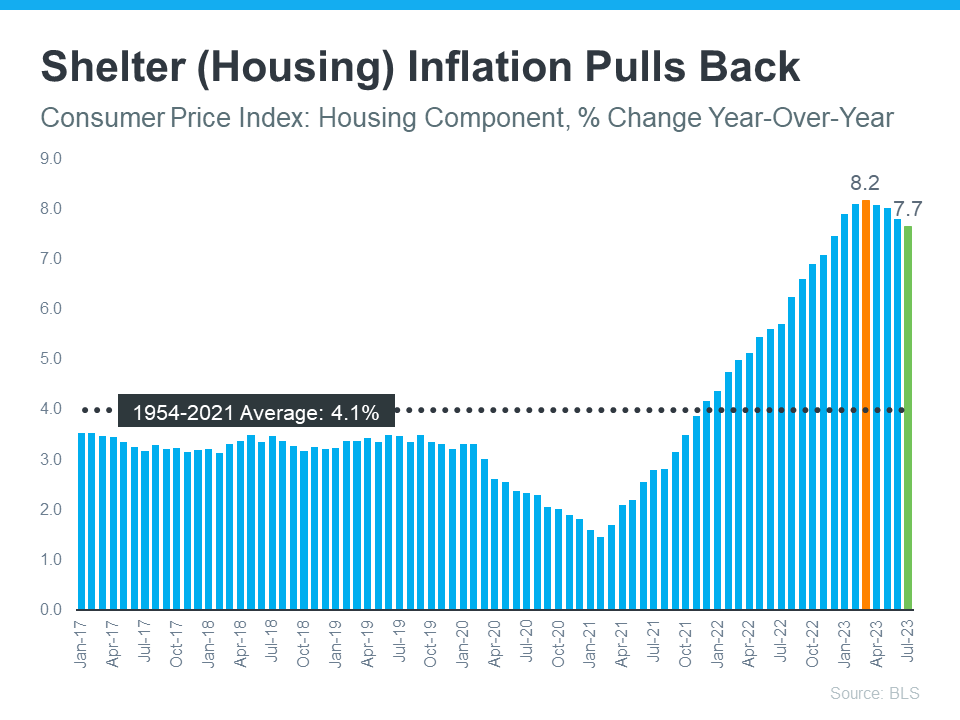
Shelter inflation is a measure of price rise in the housing market. It is based on a Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) study of renters and homeowners. Renters are asked how much they pay in rent, and homeowners are asked how much they would rent their homes for if they weren't living in them.
Shelter inflation monitors the cost of housing in the same way that general inflation measures the cost of common products. And, according to the study, housing inflation has been declining for four months in a row (see graph below):
What is the significance of this? Shelter inflation, as measured by the Consumer Price Index (CPI), accounts for almost one-third of overall inflation. As a result, changes in shelter inflation cause noticeable changes in overall inflation. As a result, the recent drop in shelter inflation may be a hint that total inflation might decrease in the coming months.
The Federal Reserve (the Fed) would be happy to see this moderation. Since early 2022, they've been attempting to bring inflation under control. While they've made some progress (it peaked at 8.9% in the middle of last year), they're still a long way from their 2% target (with the most recent report at 3.3%).
The Federal Funds Rate and Inflation
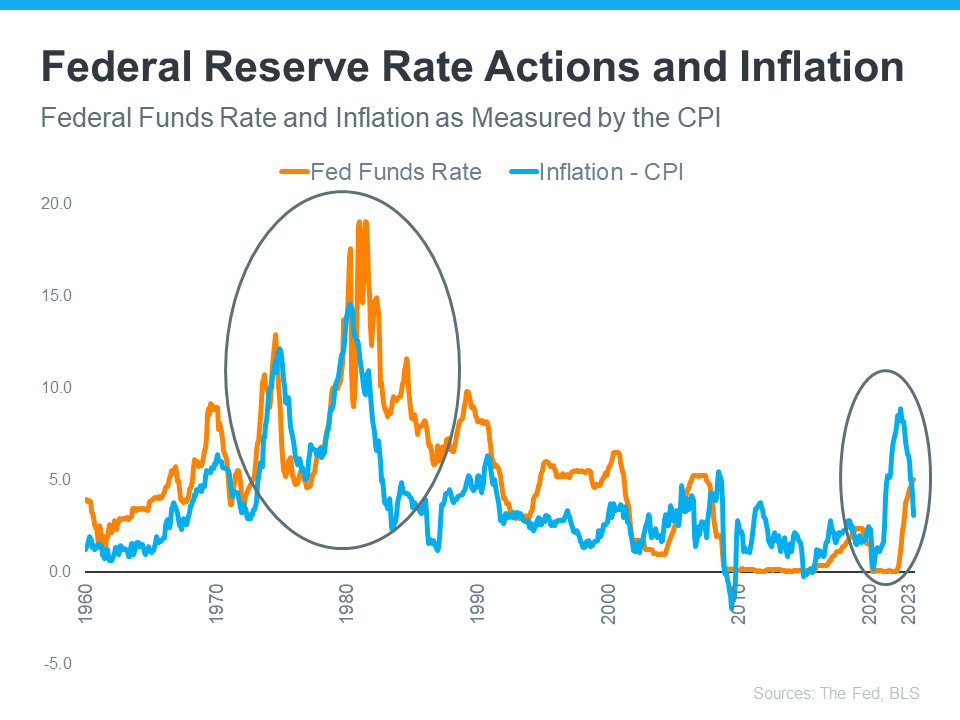
What has the Fed done to reduce inflation? The Federal Funds Rate has been raised. This interest rate has an impact on how much it costs banks to borrow money from one another. When inflation began to rise, the Fed responded by hiking the Federal Funds Rate in order to prevent the economy from overheating.
The graph below depicts the two's relationship. When inflation (shown in blue) begins to rise, the Fed boosts the Federal Funds Rate (shown in orange) to try to bring it back to their 2% target (see below):
The circled area of the graph depicts the most recent surge in inflation, the Fed's steps to raise the Federal Funds Rate to combat it, and the moderation of inflation that occurred as a result of that hike. As inflation approaches the Fed's current 2% target, the Federal Funds Rate may not need to be raised much further.
Mortgage Rates: A Better Future?
So, what does this all mean for you? While the Fed's activities do not set mortgage rates, they certainly have an impact. According to Mortgage Professional America (MPA),
“. . . mortgage rates and inflation are connected, however indirectly. When inflation rises, mortgage rates rise to keep up with the value of the US dollar. When inflation drops, mortgage rates follow suit.”
While no one can forecast the future of mortgage rates, signs of easing inflation in the economy are positive.
In conclusion
Let's connect if you're wanting to buy, sell, or simply remain updated about the housing market.





Post a comment